Microwaves, Infrared and Visible Light
Microwaves, Infrared and Visible Light
Microwaves, infrared and visible light waves also have individual uses. These types of electromagnetic radiation are also less harmful as they carry less energy than ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays.
Microwaves
Microwaves have wavelengths around 1 \text{ cm}. There are two main uses of microwaves:
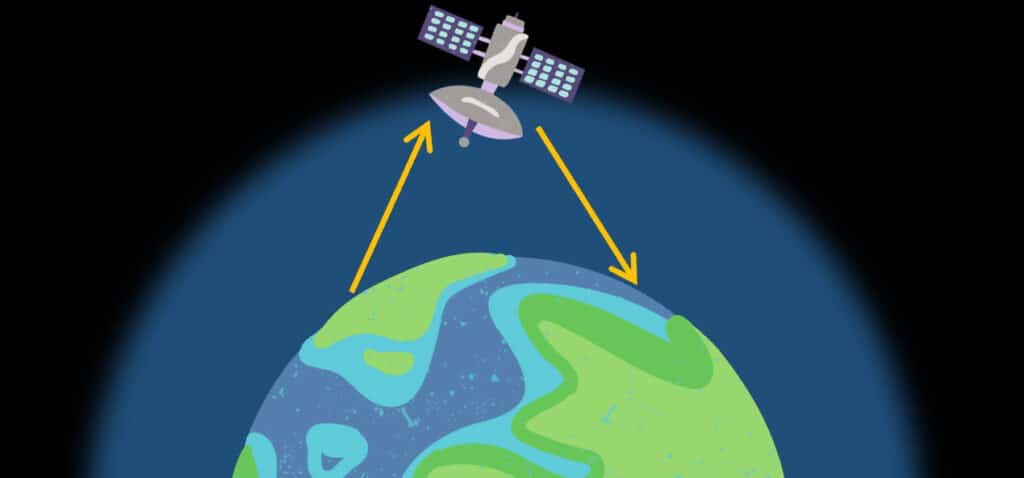
Satellite Communication
Microwaves are used to send signals to satellites which can send the signals on to distant locations. The satellites orbit the Earth, thousands of kilometres above the surface. The returned signal is received by a satellite dish.
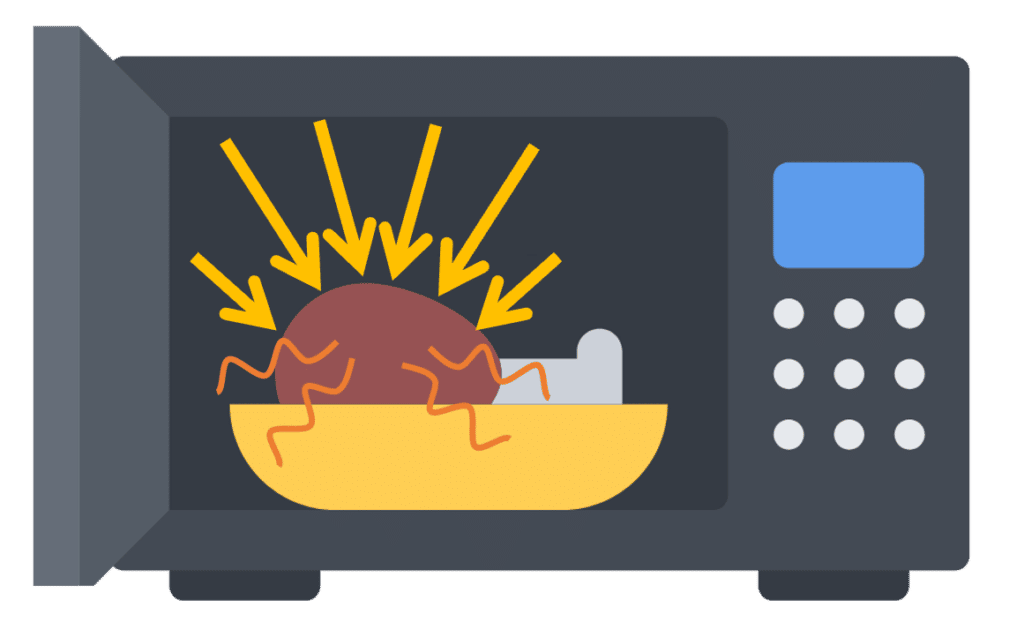
Microwave Ovens
In microwave ovens, microwave radiation is emitted by the oven and then absorbed by water molecules in the food. This energy heats up the water molecules, which also heat up the surrounding molecules via heat transfer.
Infrared Radiation
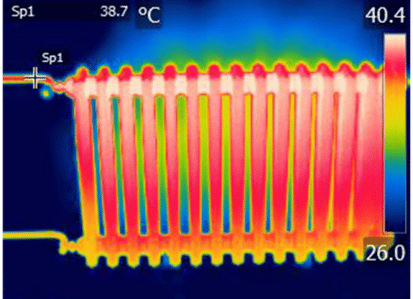
Infrared waves are emitted when objects heat up. This means that detection of infrared waves can be used to detect warm objects and measure temperature from a distance. This can be used by an infrared camera to create an image where different colours represent different temperatures, such as the one shown on the right hand side.
Objects also heat up when they absorb infrared radiation. Electric heaters and the heating element inside toasters both emit infrared radiation, along with a small amount of visible light, in order to heat up the air and your toast.
Visible Light
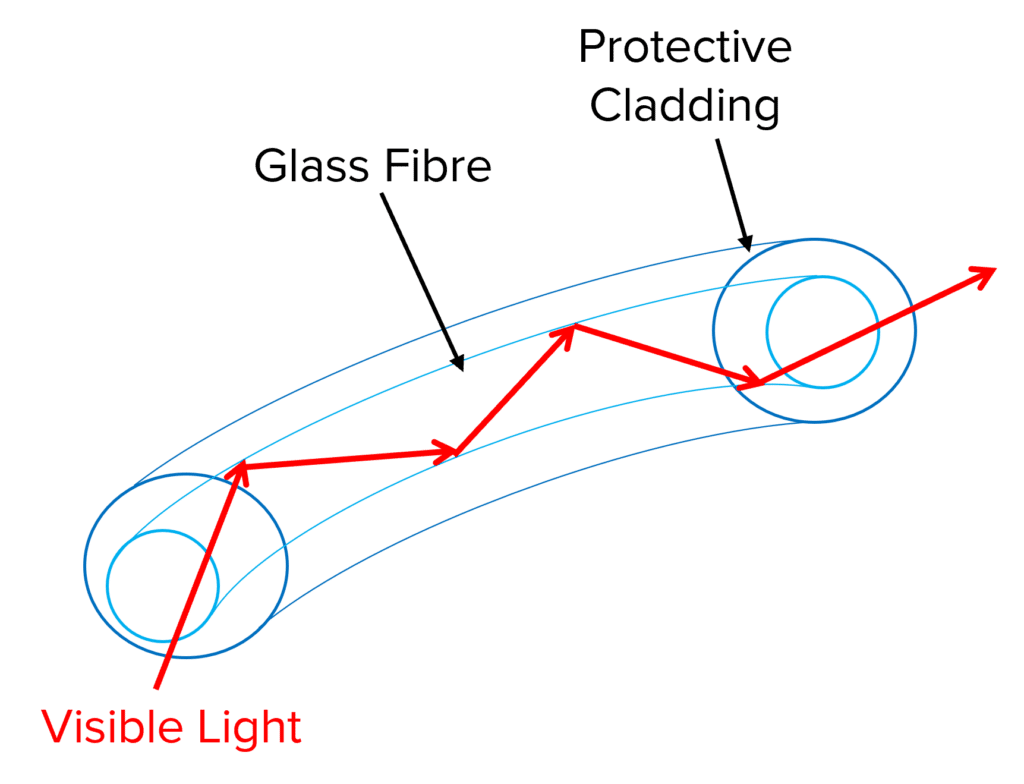
Visible light is the range of wavelengths through which we see the world. However it can also be used for communications.
Visible light is used in optical fibres made of glass to transmit information. The visible light travels along the fibre by reflecting off the inner surface of the fibre and is not refracted or transmitted through the fibre. This technology is now commonly used for internet connections.
Microwaves, Infrared and Visible Light Example Questions
Question 1: Describe how microwave ovens heat up a bowl of soup.
[3 marks]
The microwaves emitted y the oven are absorbed by water molecules in the food.
This causes a heating effect in the water molecules.
The water molecules then transfer their heat energy to surrounding molecules.
Question 2: State two uses of infrared radiation.
[2 marks]
Question 3: Describe briefly how visible light may be used to transmit information.
[2 marks]
Light is sent down optical fibres.
It travels along the fibre by reflecting off its inner surface.
Question 4: Why are visible light, infrared and microwaves less dangerous than ultraviolet, gamma rays and X-rays?
[1 mark]
They have less energy/are not ionising.
Specification Points Covered
AQA GCSE
- 4.6.2.4 Uses and applications of electromagnetic waves